🔵 NEO Update: Software Intelligence That Fills the Gaps
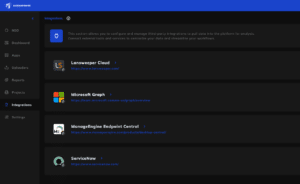
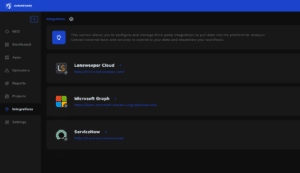
NEO Intelligence Platform Enhancements: The Engine Behind the Software Inventory Manager
The updates described below are crucial for SIM (Software Inventory Manager) as NEO is the foundational intelligence platform responsible for identifying, enriching, and standardizing all software products and versions within the SIM catalog, providing the clean, accurate data needed for effective ITAM.
Introducing major enhancements to NEO product recognition and data enrichment: 90% recognition rate through multi-layer intelligence, smart version inference that eliminates blind spots when vendor data is incomplete, 70% smaller footprint through lifecycle grouping, and automatic AI capability detection, all grounded in public, verifiable sources.
What’s New
🔵 NEO AI Capability Detection NEW
NEO now automatically identifies products with AI/ML capabilities and tracks vendor data training policies:
has_ai_capabilities: true— Product includes generative AI featuresuses_user_data_for_training: false— Microsoft’s public commitment: no customer data for training- Source: support.microsoft.com/en-gb/topic/artificial-intelligence-terms…
- Confidence: 95%
has_ai_capabilities: true— Firefly, neural filters, content-aware filluses_user_data_for_training: true— Opt-out required for content credentials- Source: adobe.com/legal/licenses-terms/adobe-gen-ai-user-guidelines
- Confidence: 92%
This helps organizations manage AI governance, data privacy compliance, and licensing for AI-enhanced products.
Platform Improvements
🎯 90% Recognition Based on Multi-Layered AI Recognition
Products are recognized through a combination of multiple intelligent matching techniques, from exact synonym matches to AI-powered semantic analysis, ensuring we identify even poorly-formatted, abbreviated, or vendor-specific product names.
This multi-layered approach achieves 90% recognition rates compared to typical 70-80% with traditional exact-match systems.
🔮 Smart Version Inference: Filling Vendor Data Gaps
The breakthrough: when vendors don’t publish lifecycle data for every patch version, we intelligently infer it from known lifecycle boundaries.
Node.js 6 → No data found
Node.js 7 → EOL Jun 2017
Node.js 6.17.1 → EOL Jun 2017
Inferred (78% confidence)
Ubuntu 22.04.3
Unknown EOL
Ubuntu 22.04.3 → EOL Apr 2027
Matched (100% confidence)
VC++ 2015-2022 → Lifecycle tied to Visual Studio 2022
VC++ 14.38.33130 → EOL Apr 2027
Inferred (88% confidence)
📦 70% Smaller Catalog Footprint
By grouping versions based on lifecycle boundaries rather than tracking every individual patch, NEO dramatically reduces catalog size while maintaining complete matching accuracy. Thousands of version strings collapse into manageable lifecycle groups, making queries faster and simpler.
Example: 2,000+ product variants consolidate to 347 unique products. Catalog updates complete in minutes instead of hours.
Grounded in Public Sources
Every lifecycle date, every inference, every AI capability flag comes from verifiable public sources:
• Product documentation
• Security advisories
• Support policy pages
• endoflife.date
• Official GitHub releases
• SPDX registries
• Community forums
• Speculation/rumors
• Paywalled databases
Why This Matters
For Security Teams
- Zero blind spots: Version inference ensures every product in your software inventory has lifecycle data, even obscure patches
- Risk prioritization: Confidence scores help focus on high-certainty threats first
- Audit trail: Every EOL date links back to official vendor sources
For IT Asset Management
- Reduced complexity: 70% smaller footprint means faster queries and simpler reporting across all devices and software
- Better coverage: 90% recognition rate vs typical 60-70% with exact-match-only systems
- AI transparency: Know which products have AI features and data policies
Real-World Results
Getting Started
The enhanced NEO engine is available now in SIM. Existing SIM catalogs will automatically benefit from version inference and AI capability detection on the next scheduled refresh. Get in touch using the form below to find out more or schedule a demo.